A level curve of a function is curve of points where function have constant values,level curve is simply a cross section of graph of function when equated to some constant values,example a function of two variables say x and y,then level curve is the curve of points (x,y),where function have constant value 19K views Admin Igcse Economics Revision Notes, O Level Economics Revision Notes 3 Comments 11,038 Views Production Possibility Curve The following is a curve representing all possible combinations of two goods that can be produced by an economy where all of its resources are fully and efficiently employedThe real wage and the natural level of employment are determined by the intersection of the demand and supply curves for labor Potential output is given by the point on the aggregate production function corresponding to the natural level of employment This output level is the same as that shown by the longrun aggregate supply curve
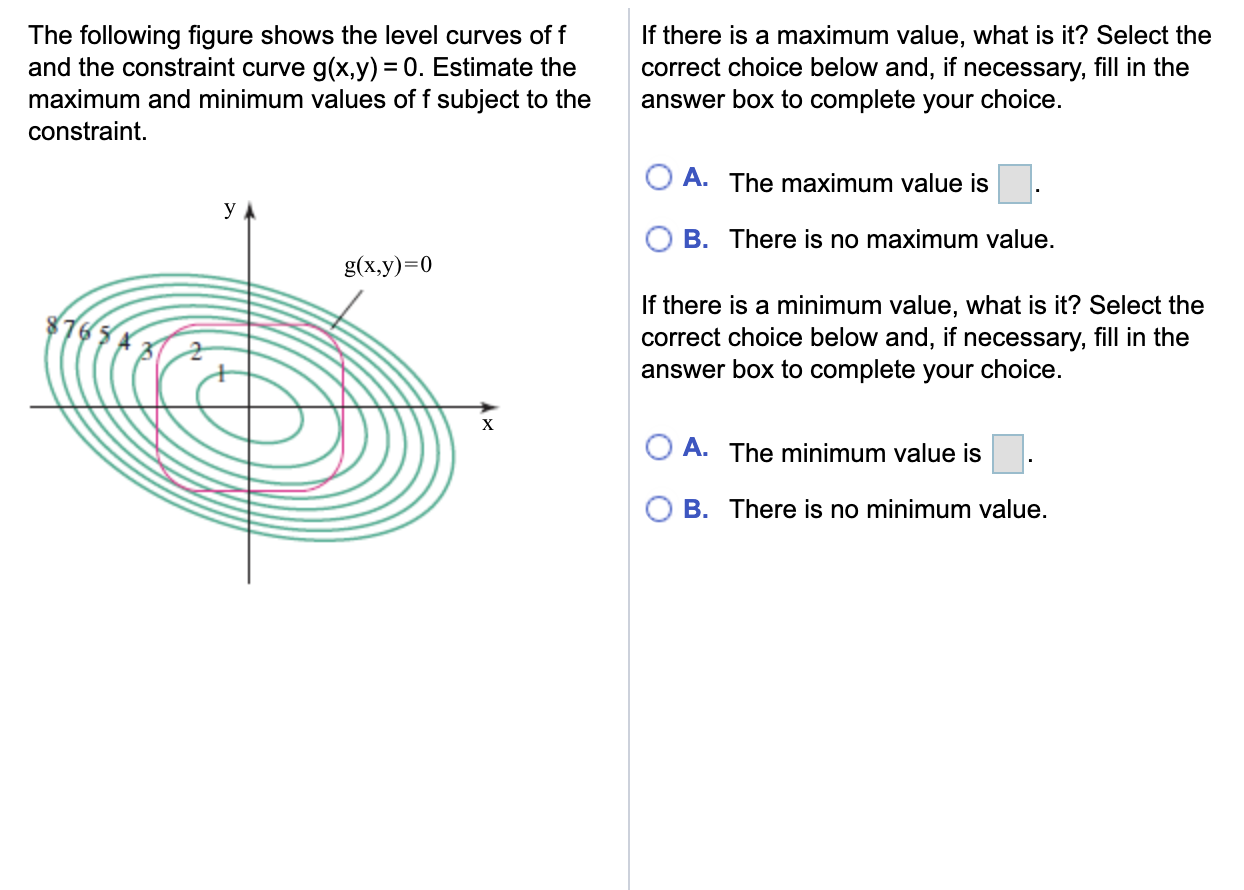
The Following Figure Shows The Level Curves Of F And Chegg Com
Level curves economics
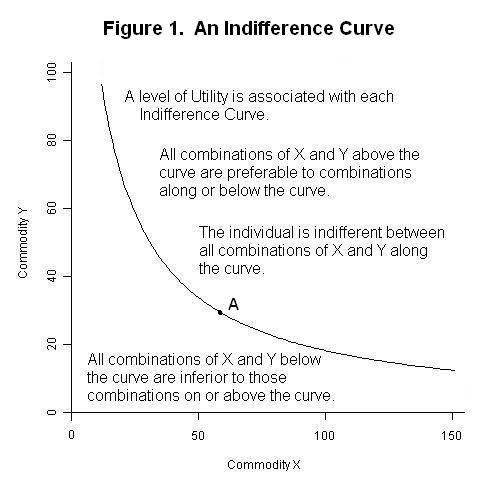
Level curves economics-In economics, an indifference curve connects points on a graph representing different quantities of two goods, points between which a consumer is indifferentThat is, any combinations of two products indicated by the curve will provide the consumer with equal levels of utility, and the consumer has no preference for one combination or bundle of goods over a different combination on the same curveThe demand curve is a line graph utilized in economics, that shows how many units of a good Inventory Inventory is a current asset account found on the balance sheet, consisting of all raw materials, workinprogress, and finished goods that a or service will be purchased at various prices The price is plotted on the vertical (Y) axis while the quantity is




Indifference Curves Different Combinations Of The Two Goods The Same Level Of Utility Is Derived From Consump Indifference Curve Indifference Teaching Tools
An example of a demand curve shifting The shift from D1 to D2 means an increase in demand with consequences for the other variables In economics, the demand curveBy the use of level curves we can represent these graphs in two dimensions is called the level curve with a (function) value equal to k ( x, y, z) coordinate system Remark 2 Level curves of the same function with different values cannot intersect Remark 3 Level curves of utility functions are called indifference curvesEconomics Stack Exchange is a question and answer site for those who study, teach, research and apply economics and econometrics It only takes a minute to sign up Thus, the curves in the level set are closed curves (not sure why) All closed curves
Definition The Lorenz curve is a way of showing the distribution of income (or wealth) within an economy It was developed by Max O Lorenz in 1905 for representing wealth distribution The Lorenz curve shows the cumulative share of income from different sections of the populationThat is, the breakeven forward curve collapsed onto itself and has been essentially flat for over seven years (that is, the lines are almost on top of each other in the second part of theHow the cost curves are derived It is important to understand why the cost curves look like they do The concept of Diminishing marginal Returns is the one from which we derive the cost curves Look at the two diagrams below The top diagram shows a sketch of the marginal cost curve and the average cost curve
In economics, output is the quantity of goods and services produced in a given time period The level of output is determined by both the aggregate supply and aggregate demand within an economy National output is what makes a country rich, not large amounts of moneyThe fundamental problem of scarcity challenges us to think about an allocation mechanism to determine what is produced and who consumes it We will discuss scarcity and allocation mechanisms In this course, we will focus on markets and prices as the solution to this resource allocation problem 111 Scarcity and its Implications 1955 112While the Lorenz curve is most often used to represent economic inequality, it can also demonstrate unequal distribution in any system The farther away the curve is




Level Curves And Implicit Differentiation Studocu




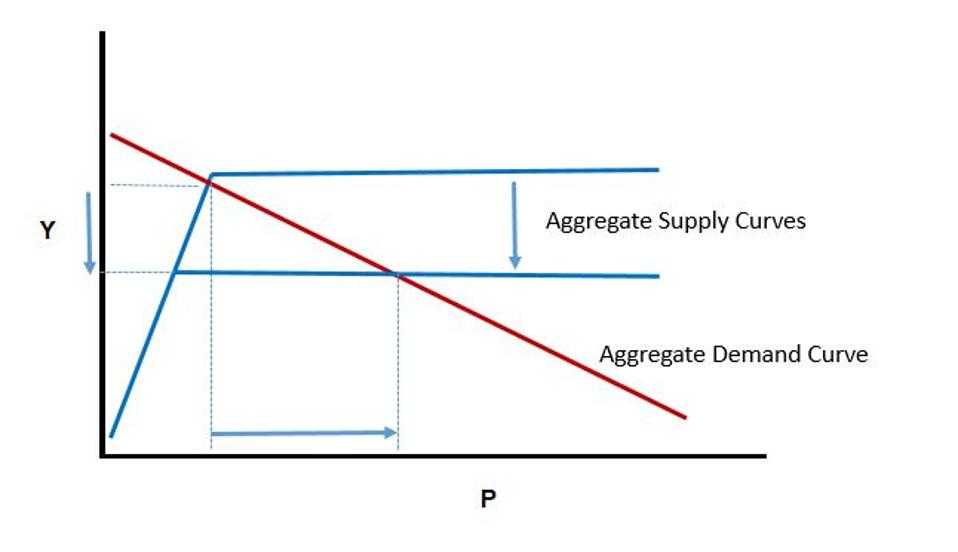
Combining Ad And As Supply Curves
The LRAC is a a cost curve which shows the average cost per unit of production over varying amounts of output in the longrun, and can be calculated by total costs divided by total output Economies of Scale is the condition where the firm is able to reduce average costs (LRAC) in the long run, when output of goods/services increasesFree ebook http//tinyurlcom/EngMathYT How to sketch level curves and their relationship with surfaces Such ideas are seen in university mathematics andSupply does not capture all the costs with the S curve are overallocated to the production of this product By shifting costs to the consumer, the firm enjoys S 1 curve and Q e, (optimum output ) Q e Q o MSB P Q S MPB shown by the intersection of D Spillover Benefits Underallocation of resources when external benefits are present and the
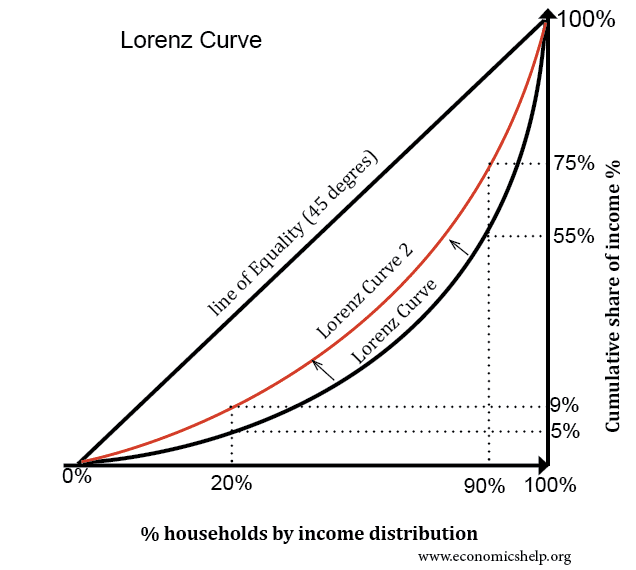



Lorenz Curve Economics Help
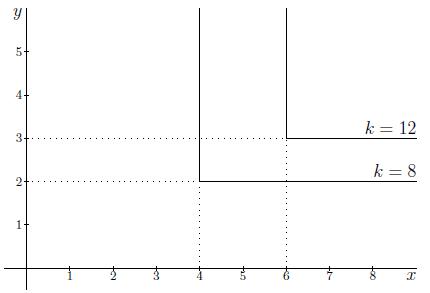



Exercise 5 Wiskunde Op Tilburg University
As with the last LearnIt, it is worth looking at these relationships in more detail Look at this table below Q is output per week for a firm making computer laser printers The cost figures are all in pounds and rounded to the nearest pound Q TFC TVC AFC AVC TC AC MC 0 500 0 500 1 500 100 500 100 600 600 100 2 500 180 250 90 680 340 80 3 500 250 167 750 250 70 4Demand Classical economics presents a relatively static model of the interactions among price, supply and demand The supply and demand curves which are used in most economics textbooks show the dependence of supply and demand on price, but do not provide adequate information on how equilibrium is reached, or the time scale involvedThat is, the slope of the level curve through (cx 0, cy 0) at the point (cx 0, cy 0) is exactly the same as the slope of the level curve through (x 0, y 0) at the point (x 0, y 0), as illustrated in the following figurex → y ↑ 0 x 0 cx 0 y 0 cy 0 In this figure, the red lines are two level curves, and the two green lines, the tangents to the curves at (x 0, y 0) and at (cx 0, cy 0), are




1 Objective Functions In Two Variables Partial Differentiation




The Economy Unit Economics Of The Environment
These curves are used to model the general equilibrium and have been given two equivalent interpretations First, the ISLM model explains the changes that occur in national income with a fixed shortrun price level Secondly, the ISLM curve explains the causes of a shift in the aggregate demand curveIf we draw the locus in the \(xy\)plane of \((x,y)\) pairs for which the function has the value \(z_{0}\), the corresponding curve is called the level curve of the function (See Simon and Blume, p 280) In economics frequently used level curves are indifference curves and isoquantsA long run average cost curve is known as a planning curve This is because a firm plans to produce an output in the long run by choosing a plant on the long run average cost curve corresponding to the output It helps the firm decide the size of the plant for producing the desired output at the least possible cost



What Is A Level Curve Quora




Economics Chart The Following Graph Shows The Economy In Long Run Equilibrium At The Price Level Of Homeworklib
The total utility curve in Figure 71 "Total Utility and Marginal Utility Curves" shows that Mr Higgins achieves the maximum total utility possible from movies when he sees six of them each month It is likely that his total utility curves for other goods and services will have much the same shape, reaching a maximum at some level ofThe Phillips curve is the relationship between inflation, which affects the price level aspect of aggregate demand, and unemployment, which is dependent on the real output portion of aggregate demand Consequently, it is not farfetched to say that the Phillips curve and aggregate demand are actually closely relatedLet f be a function of two variables, and c a constant The set of pairs (x, y) such that f (x, y) = c is called the level curve of f for the value c




Aggregate Demand Ad Curve




Phillips Curve Fiscal Policy Economics Online Economics Online
The IS curve is the schedule of combinations of the interest rate and the level of income such that the goods market is in equilibrium 2 The IS is negatively sloped because an increase in the interest rate reduces planned (desired) investment spending and therefore reduces aggregate demand, thereby lowering the equilibrium level of incomeThe Lorenz curve is a simple graphical / visual representation of income or wealth distribution developed by American economist Max Lorenz in 1905#aqaeconoThe aggregate supply curve depicts the quantity of real GDP that is supplied by the economy at different price levels The reasoning used to construct the aggregate supply curve differs from the reasoning used to construct the supply curves for individual goods and services
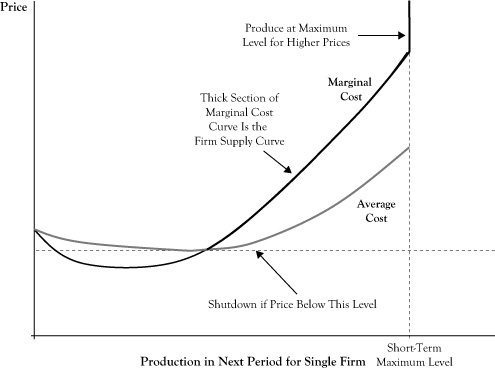



Firm Supply Curves And Market Supply Curves




Level Curves Indifference Curves Isoquants Youtube
What is a Demand Curve?Upward sloping (also known as normal yield curves) is where longerterm bonds have higher yields than shortterm ones While normal curves point to economicEconomics Revision You can find summary notes and past papers for each of the modules and exam boards below



Other Instances Of Level Curves
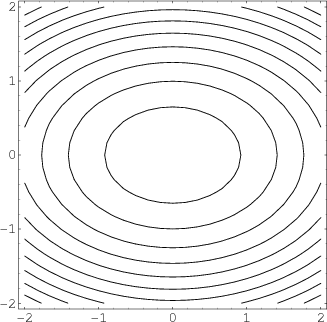



Level Sets Math Insight
This requires that the level of income rise at the given world real interest rate to bring desired money holdings back into line with the unchanged money supply and preserve asset equilibriumthe LM curve shifts to the right Overall equilibrium will occur where the IS and LM curves crossIn economics, the SRAS curve is a basic concept Essentially it explains the relationships between a firm's supplied quantity and the corresponding prices The relationship of the economy in its entirety is also described by the SRAS curve There are two models that support SRAS curve and these are the stickyprice and the stickywage model An indifference curve depicts a line representing all the combinations of two goods that consumers place equal value That is to say, they would be indifferent to either good The consumer has no preference for either combination of goods on the same line because they are understood to provide the same level of utility to the consumer
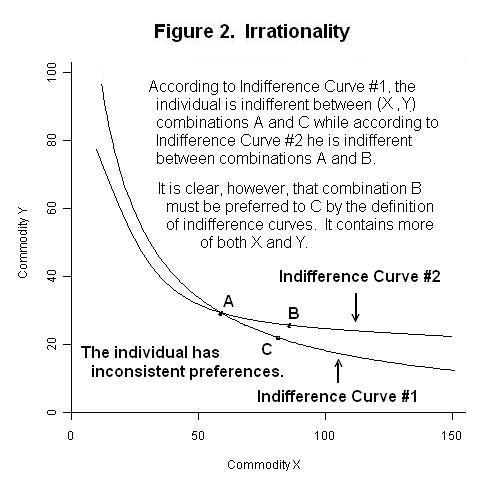



Indifference Curves
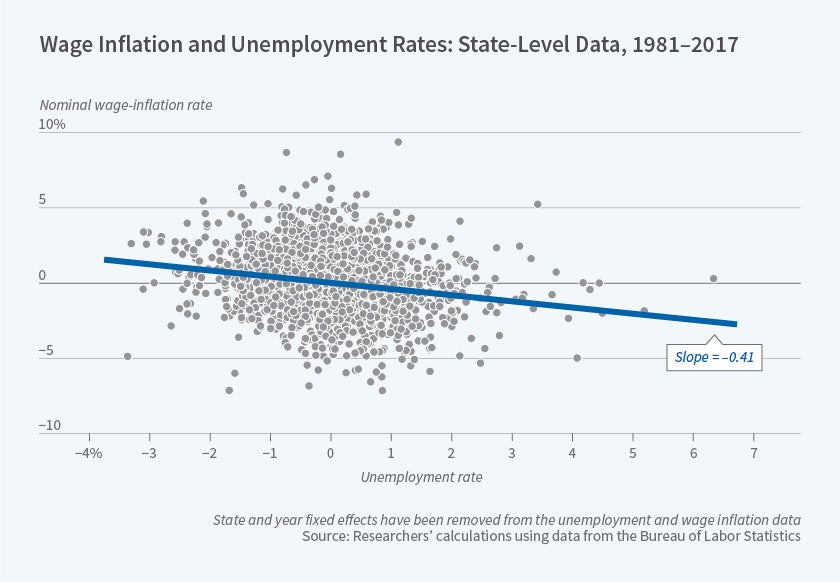



Is The Phillips Curve Still A Useful Guide For Policymakers Nber
The Phillips Curve traces the relationship between pay growth on the one hand and the balance of labour market supply and demand, represented by unemployment, on the other It has been a staple part of macroeconomic theory for many years Students often encounter the Phillips Curve concept when discussing possible tradeoffs between macroeconomic objectivesExplain the ways in which Fiscal Policy and Monetary Policy interact by using Keynesian IS and LM curves Discuss the impact of an expansionary Fiscal Policy and Monetary Policy on the overallThe firm's revenue in two different points of the demand curve can be explained at higher price for instance at price $550 demand is 5000 At this level revenue is =($550*5000) = $2,750,000 But in inelastic portion when price is $300, demand is At this level revenue is = ($300*)




Level Curves For The Symmetric Mean Of Order R X 2 Download Scientific Diagram
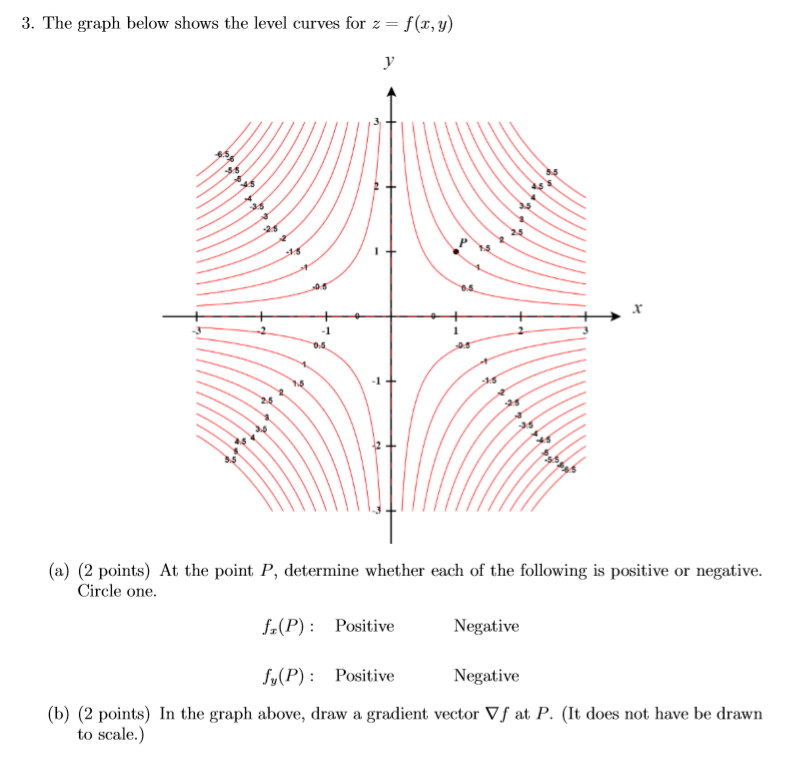



3 The Graph Below Shows The Level Curves For Z Chegg Com
An Economics Topics Detail By Arnold S Kling What Is Aggregate Supply?Cambridge International AS and A Level Economics Coursebook with CDROM ISBN Format Mixed media product Learning Stage A level, AS level, level Available from Nov 14 Out of Stock £1750 Cambridge International AS and A Level Economics Revision Guide ISBNAggregate supply is the relationship between the overall price level in the economy and the amount of output that will be supplied As output goes up, prices will be higher We draw attention to factors that shift the aggregate supply curve An adverse
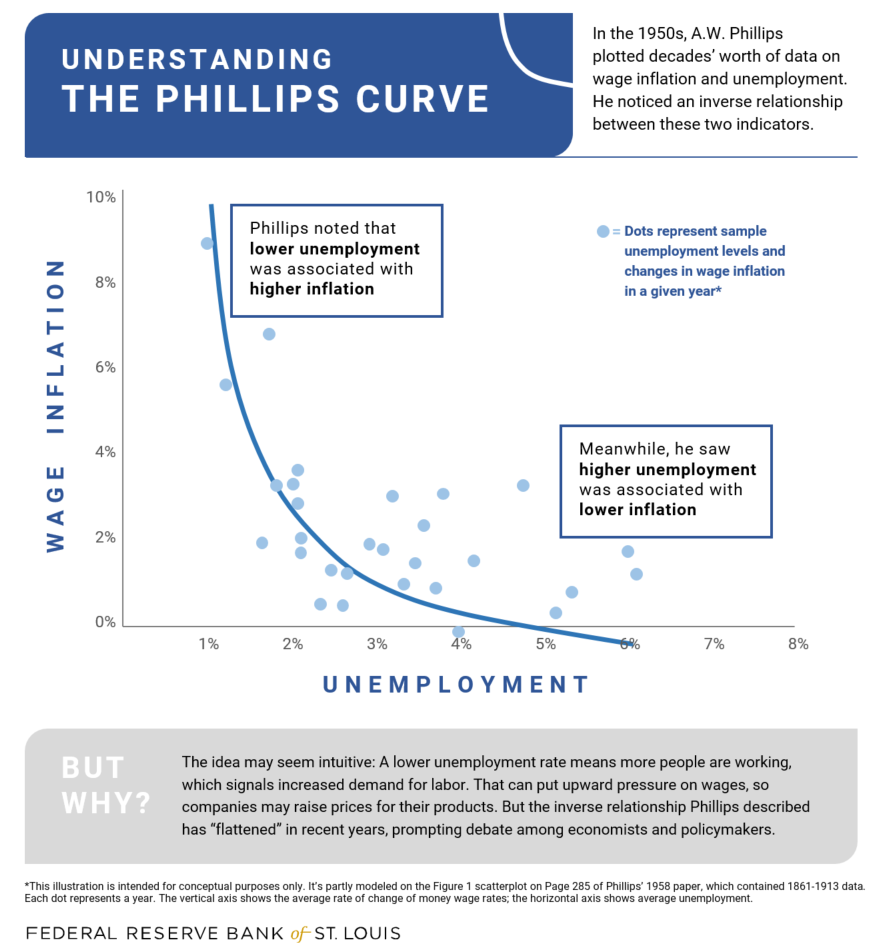



What S The Phillips Curve Why Has It Flattened St Louis Fed
/Kuznets_curve-copy-56a27de33df78cf77276a802.jpg)



Understanding Kuznets Curve
The Kuznets curve is a hypothetical curve that graphs economic inequality against income per capita over the course of economic development (which was presumed to correlate with time) This curve is meant to illustrate economist Simon Kuznets' () hypothesis about the behavior and relationship of these two variables as an economy First, there is a sharp and persistent level shift down after December 13 Second, there is a striking crosssectional compression of breakeven forwards;The Laffer Curve is a (supposed) relationship between economic activity and the rate of taxation which suggests there is an optimum tax rate which maximises total tax revenue Laffer Curve




Toward Effective Economic Policy For The 21st Century Opiniopro



Demand Curve
Igcse Economics Revision Notes, O Level Economics Revision Notes 1 Price Elasticity Of Demand, measures the responsiveness of demand to a change in price The formula used to calculate (PED) is Q1 = Old Quantity Q2 = New Quantity P1 = Old Price P2 = New Price If the answer using the above formula is less than 1 than theIf it is further assumed that the economy is fully employing all of its resources, the equilibrium level of real GDP, Y *, will correspond to the natural level of real GDP, and the LAS curve may be drawn as a vertical line at Y *, as in FigureThis quiz and worksheet will gauge your understanding of indifference curves in economics The quiz will also assess your comprehension of concepts like




Indifference Curves Different Combinations Of The Two Goods The Same Level Of Utility Is Derived From Consump Indifference Curve Indifference Teaching Tools



The Study Economics For Ma Ignou Microeconomics Macroeconomics Econometrics Mathmatical Economics Graphical Representation Of Functions
Production Possibility Curve O Level Economics 2281 and IGCSE Economics 0455 Best Notes and Resources With Explanation Posted by Hunain Zia Categories CAIE (Cambridge Assessment International Examination) , Economics (0455) , Economics (2281) , Free Education , International General Certificate of Secondary Education (IGCSE) , Notes Sequential Easy First Hard First Play as Quiz Flashcard or Create Online Exam There are questions in this test from the Economics section of the CFA Level 1 syllabus You will get 30 minutes to complete the test Questions and Answers Remove Excerpt Removing question excerpt is a premium featureLevel sets show up in many applications, often under different names For example, an implicit curve is a level curve, which is considered independently of its neighbor curves, emphasizing that such a curve is defined by an implicit equationAnalogously, a level surface is sometimes called an implicit surface or an isosurface The name isocontour is also used, which means a contour of
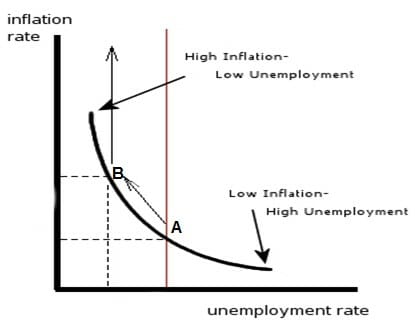



Phillips Curve Learn How Employment And Inflation Are Related
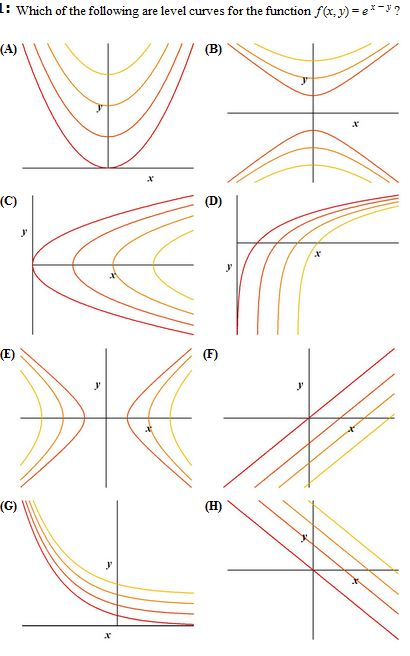



Which Of The Following Are Level Curves For The Chegg Com
Unit 1 of Cambridge A Level Economics (Basic Economic Ideas) Tutorials have been uploaded to cover the syllabus contents of the Unit 1 of Cambridge A Level Economics ( Basic Economic Ideas) The tutorials cover the following topics Scarcity, choice and resource allocation Different allocative mechanisms Production possibility curves



Economic Growth And The Aggregate Supply Curve




The Economy Leibniz Isoprofit Curves And Their Slopes




Level Curves Wiskunde Op Tilburg University
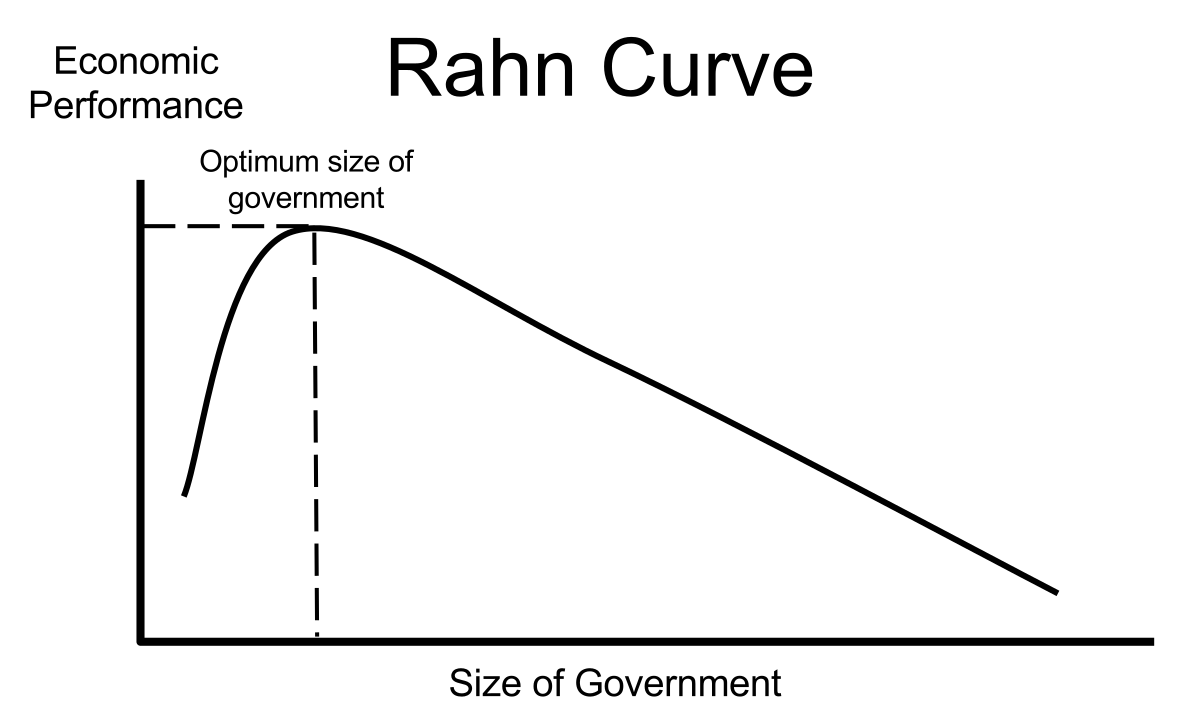



Rahn Curve Wikipedia



1
(182).jpg)



Test On Economics For Cfa Level 1 Proprofs Quiz




2 Measuring The Economics Of Biofuel Availability



What Is A Level Curve Quora
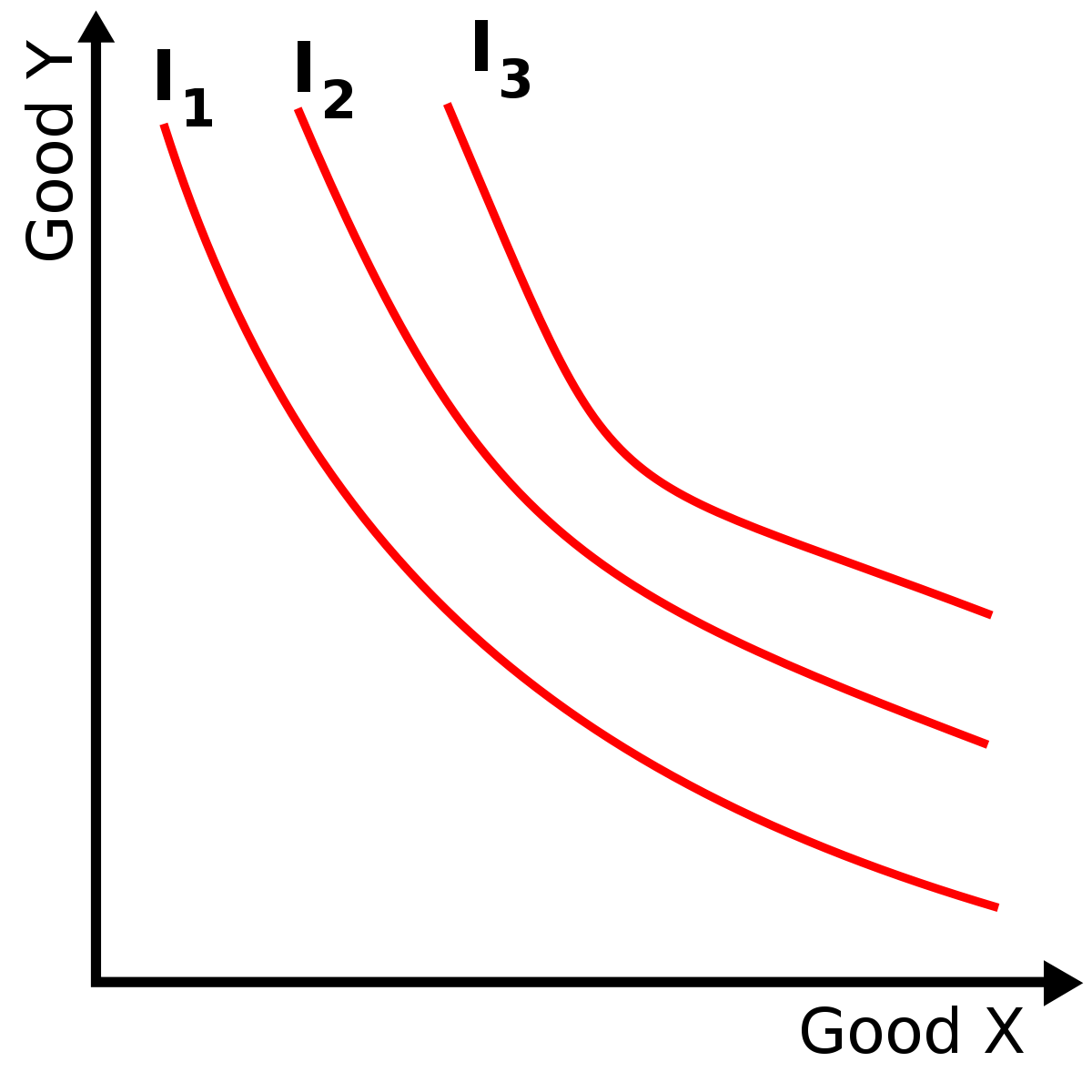



Indifference Curve Wikipedia




Level Curves
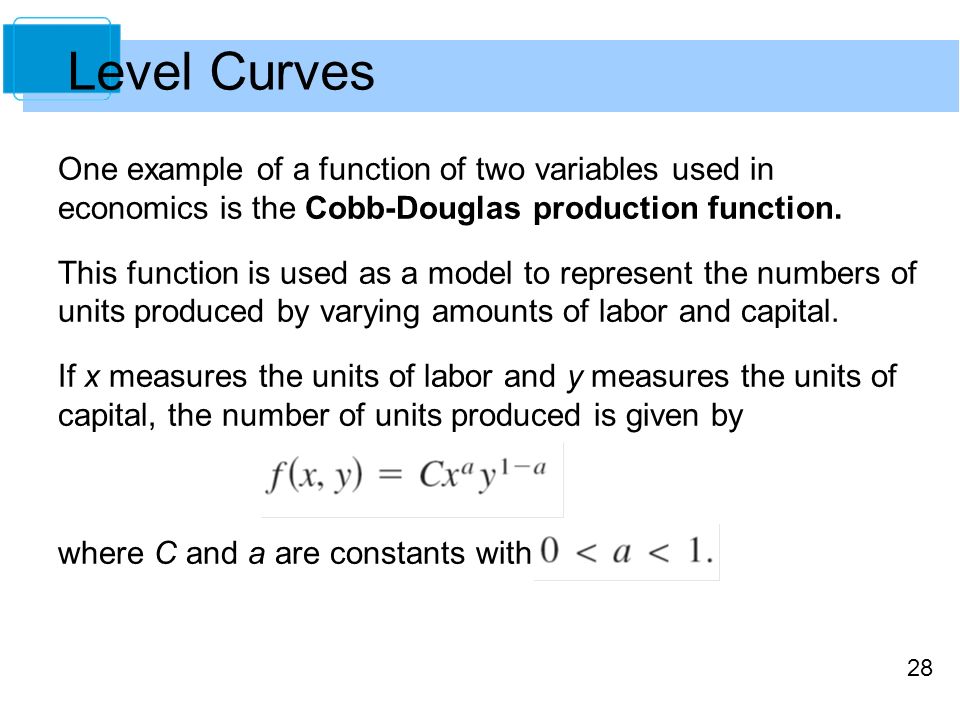



Functions Of Several Variables Ppt Video Online Download
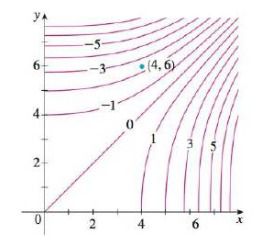



Sketch The Gradient Vector F 4 6 For The Function F Whose Level Curves Are Shown Explain How You Chose The Direction And Length Of This Vector Bartleby
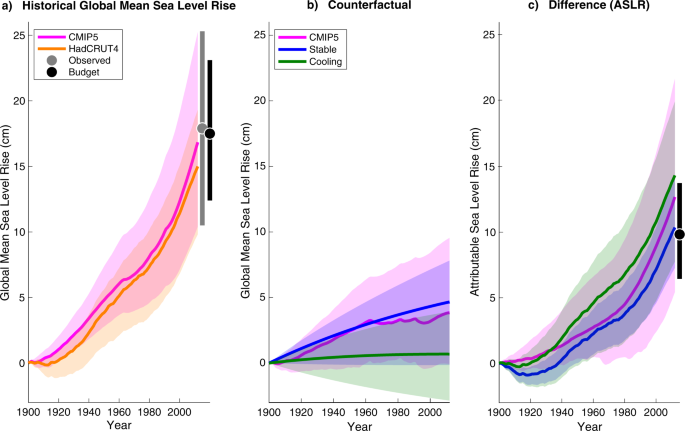



Economic Damages From Hurricane Sandy Attributable To Sea Level Rise Caused By Anthropogenic Climate Change Nature Communications
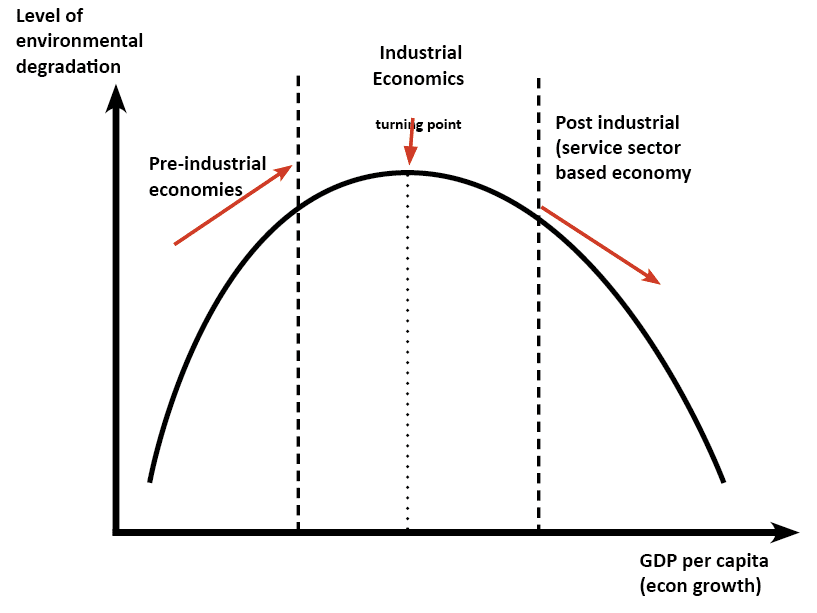



Environmental Kuznets Curve Economics Help




The Community Indifference Curves Trade Equilibrium Economics




The Changing Phillips Curve In The Uk Economy Tutor2u



Http Www Ams Sunysb Edu Jiao Teaching Ams261 Fall12 Lectures Larcalc9 Ch13 Pdf




Economic Thresholds And Economic Injury Levels Radcliffe S Ipm World Textbook
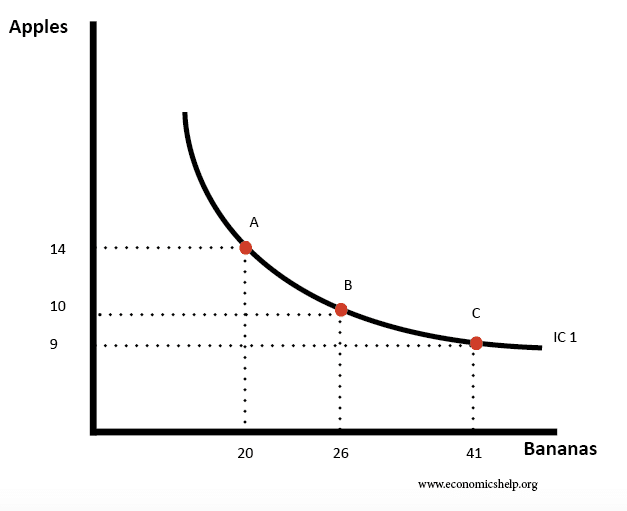



Indifference Curves And Budget Lines Economics Help
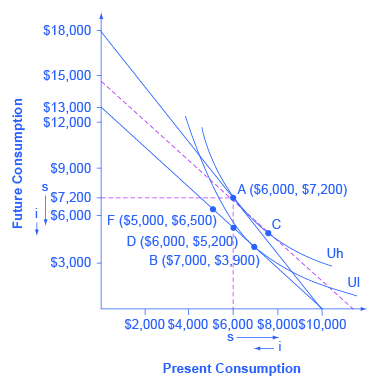



Appendix B Indifference Curves Principles Of Economics
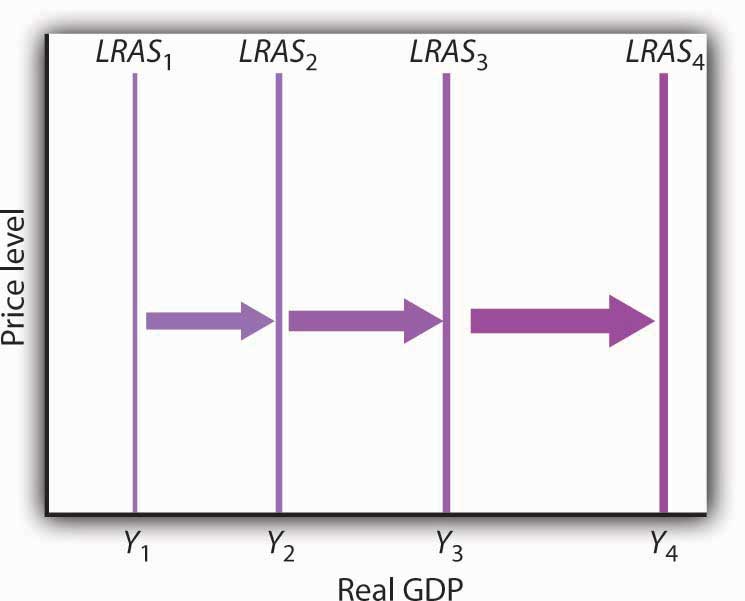



23 2 Growth And The Long Run Aggregate Supply Curve Principles Of Economics
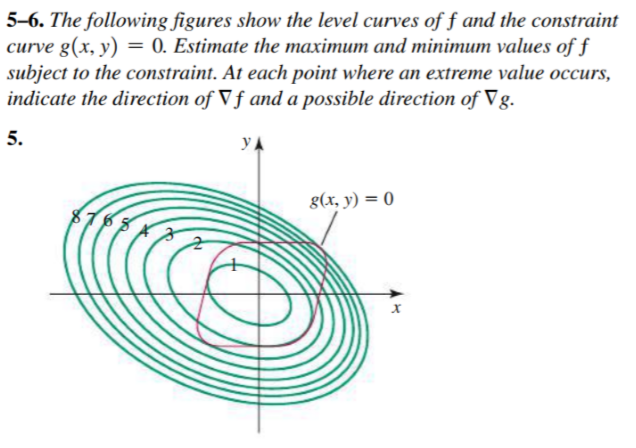



5 6 The Following Figures Show The Level Curves Of F Chegg Com



1




The Following Figure Shows The Level Curves Of F And Chegg Com



Equilibrium Level Of National Income




Not Long Ago The Canadian Edition Of A Famous Textbook On Principles Essay




Aggregate Supply And Demand Curves Economics Assignment Help Economics Homework Economics Project Help




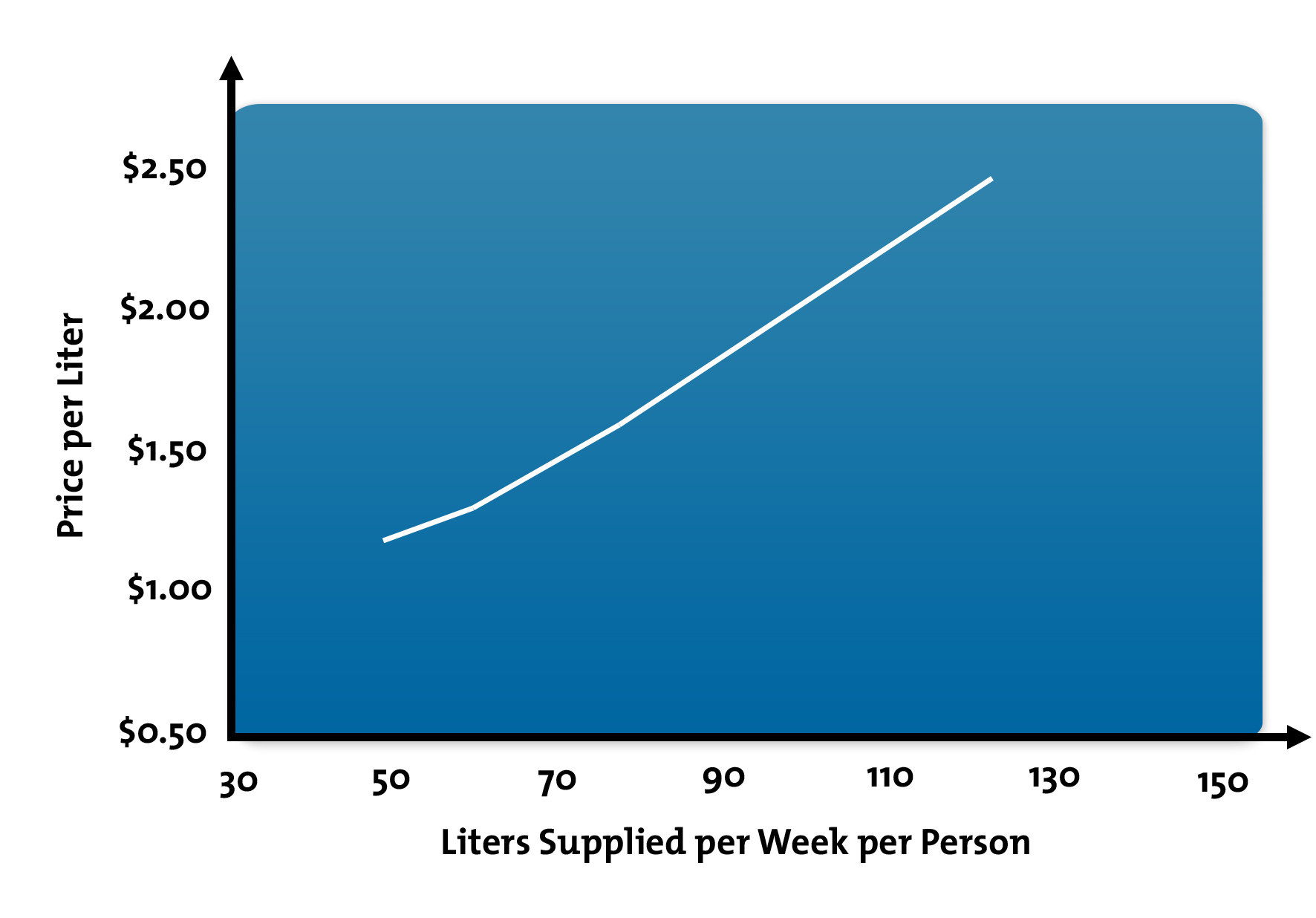
Supply Curve Definition Graph Facts Britannica



Great Depression Economics 101 Qnewshub



Indifference Curves



What Are Supply And Demand Curves From Mindtools Com
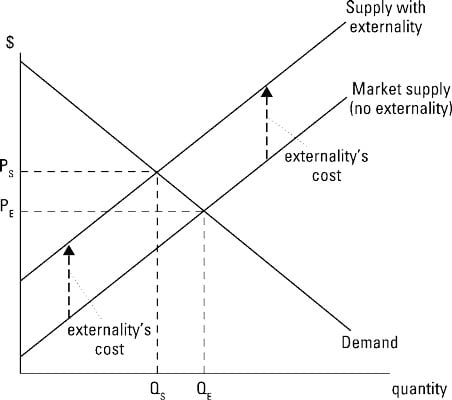



Basics Of Externalities In Managerial Economics Dummies
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/supply_curve_final-465c4c4a89504d0faeaa85485b237109.png)



Supply Curve Definition




1 Objective Functions In Two Variables Partial Differentiation



1
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Kuznets_curve-copy-56a27de33df78cf77276a802.jpg)



Understanding Kuznets Curve



Economic Interpretation Of Calculus Operations Univariate




S 1 Igcseo Level Economics 1 1 The
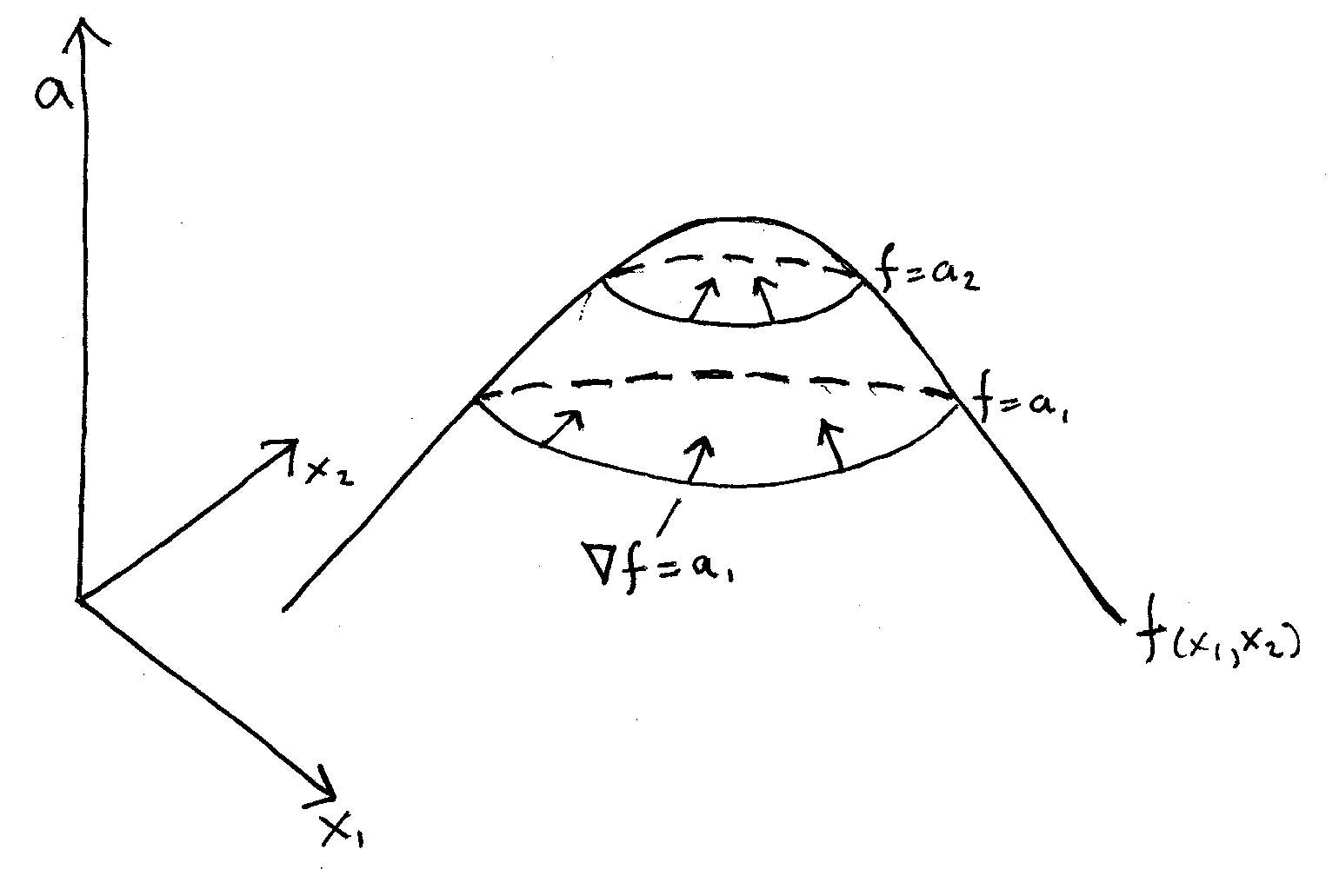



A Simple Explanation Of Why Lagrange Multipliers Works By Andrew Chamberlain Ph D Medium
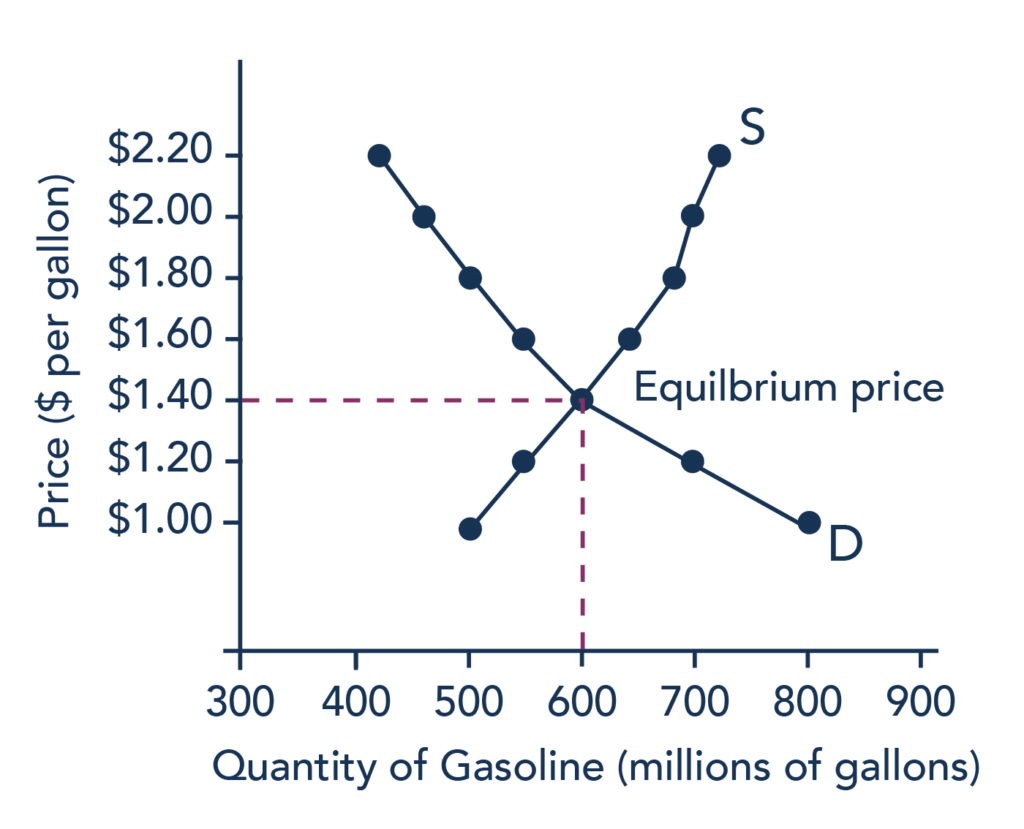



Equilibrium Price And Quantity Introduction To Business




Supply And Demand Definition Example Graph Britannica
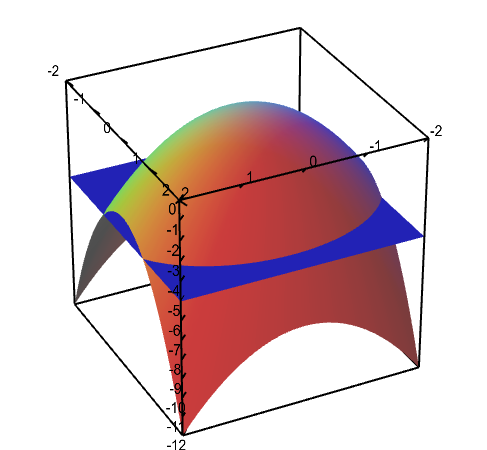



Level Sets Math Insight



Production Possibility Curve Economics




Lagrange Multipliers
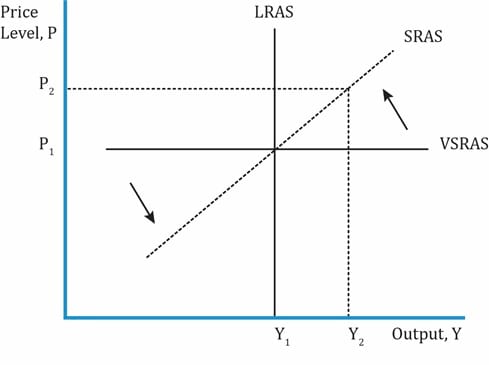



Aggregate Output Prices And Economic Growth Ift World




190 Economics Ideas In 21 Economics Managerial Economics Business And Economics
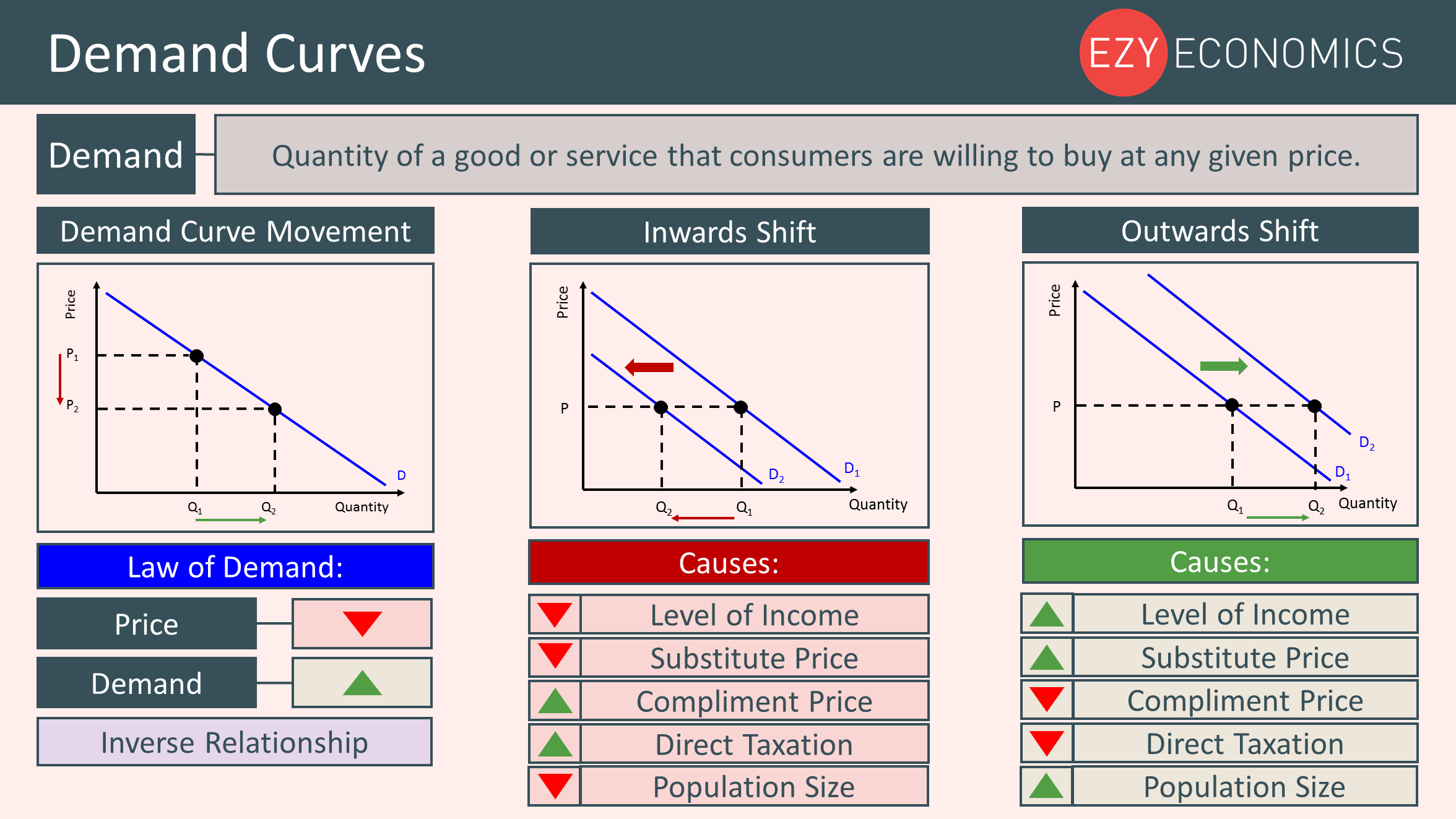



Education Resources For Teachers Schools Students Ezyeducation




Some Examples Of Graphs Used In The Problems A Level Curves Of A Download Scientific Diagram




Level Curves And Implicit Differentiation Studocu




Lecture 36 Functions Of Two Variables Visualizing Graph Level Curves Contour Lines Video Lecture By Prof Prof Inder Kumar Rana Of Iit Bombay




Aggregate Demand Ad Curve



Applications Of Integrals In Economics




1 6 Functions And Level Curves In Rn The Basics Of The Set Theory Functions In Rn Coursera



Contour Maps Article Khan Academy




A Level Economics Notes As Unit 1 Demand And Supply Curves In A Market And The Equilibrium
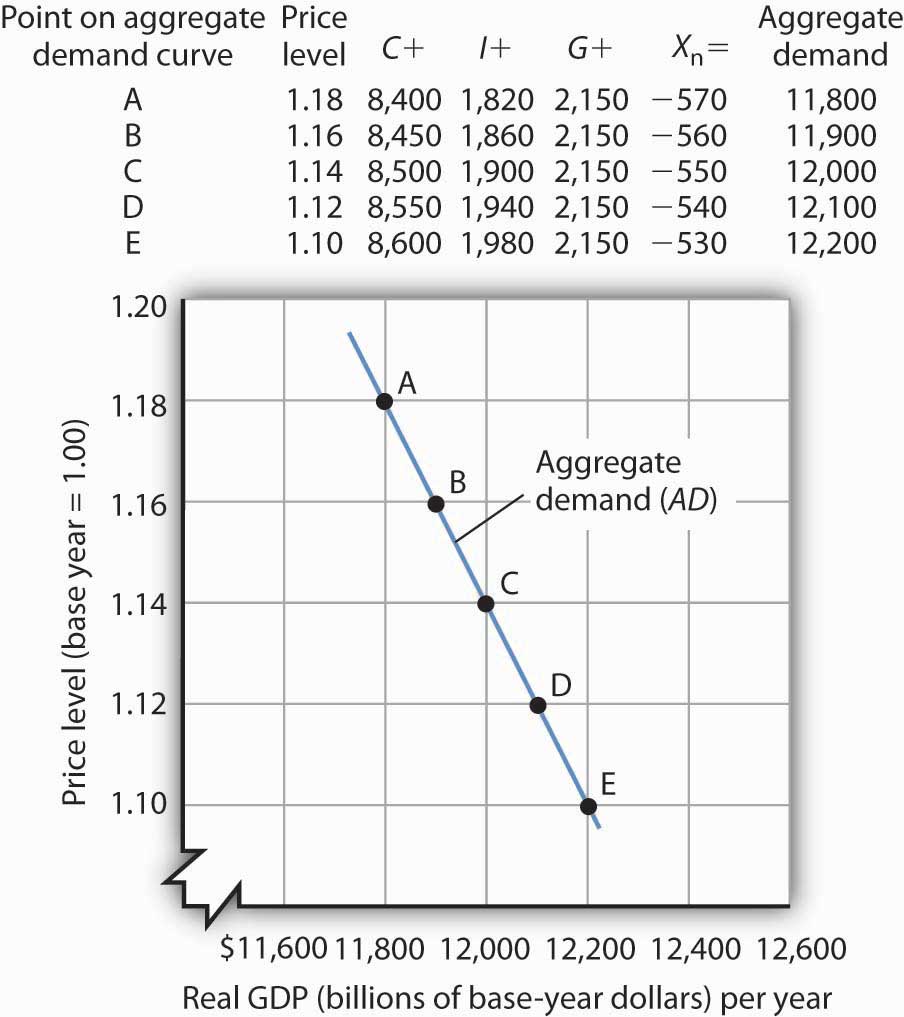



The Slope Of The Aggregate Demand Curve
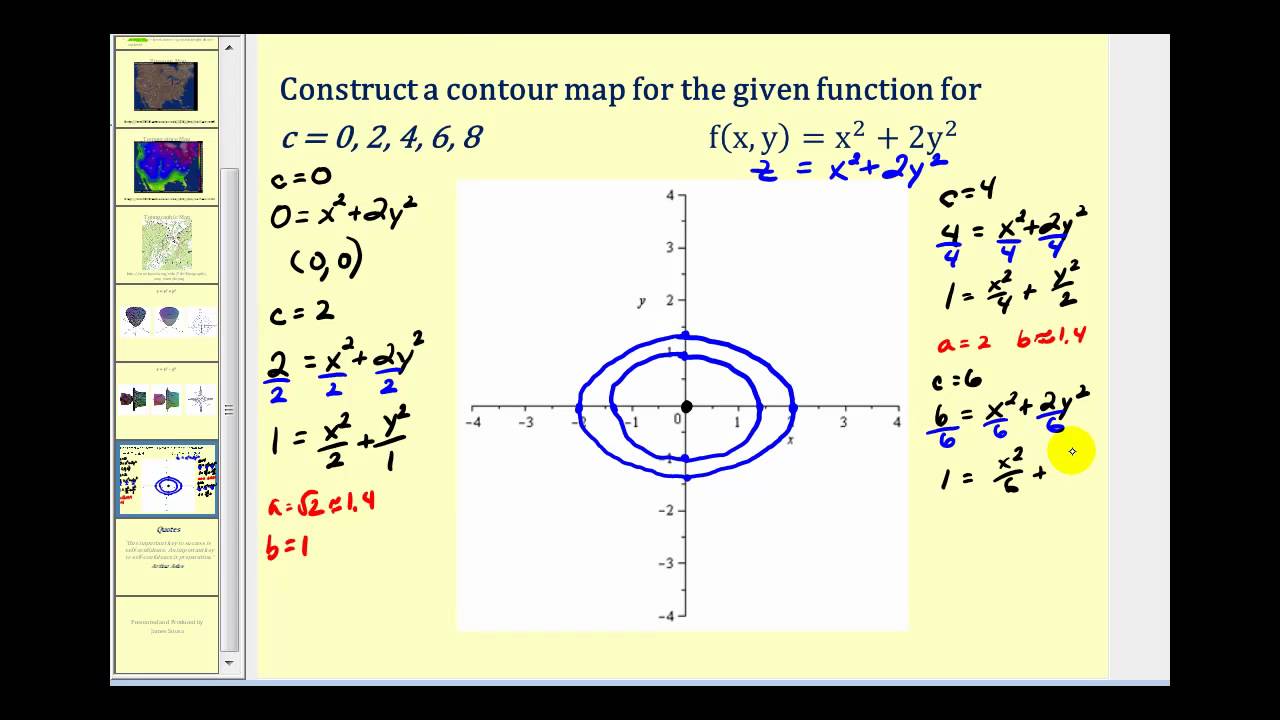



Level Curves Of Functions Of Two Variables Youtube
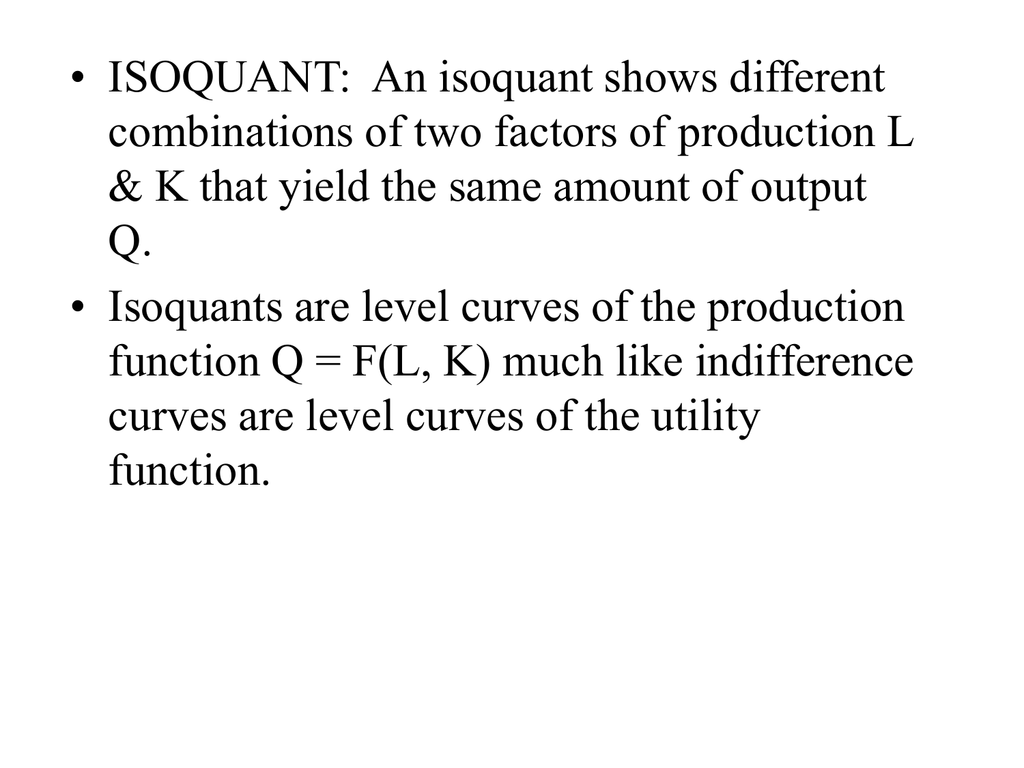



Production Isoquants Etc



1




Economics 101 What Is The Production Possibility Frontier Learn How The Production Possibility Frontier Can Be Useful In Business 21 Masterclass



2




Understanding Economic Growth Video Khan Academy




Indifference Curve Wikipedia
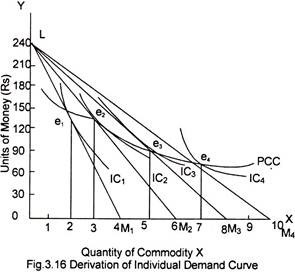



Derivation Of Individual Demand Curve With Diagram Economics




Laffer Curve Tutor2u




Aggregate Supply Model Economics Online Economics Online




Budget Lines Indifference Curves Equimarginal Principle Economics A Level Ppts 49 Slides Teaching Resources
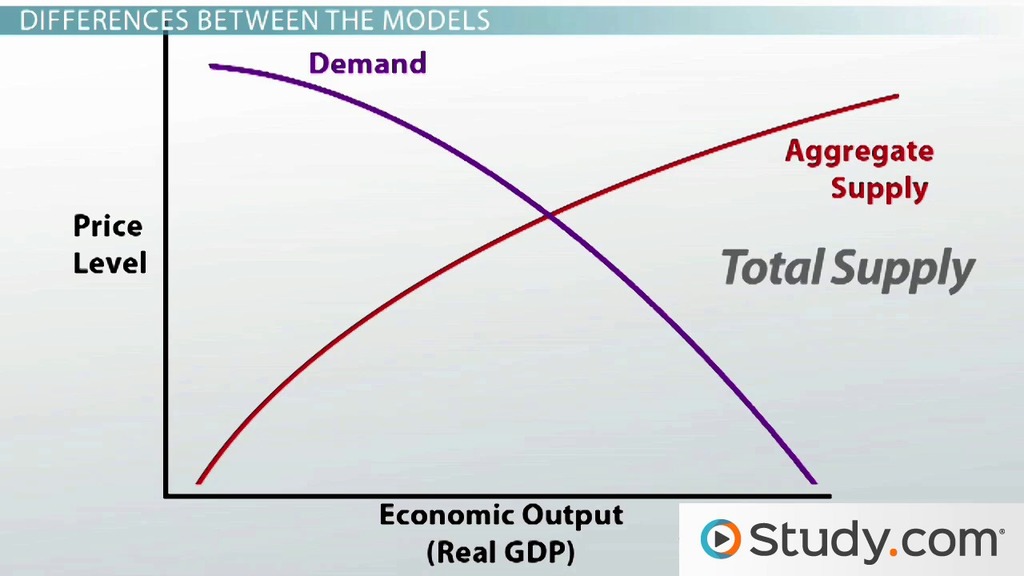



Supply And Demand Curves In The Classical Model And Keynesian Model Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
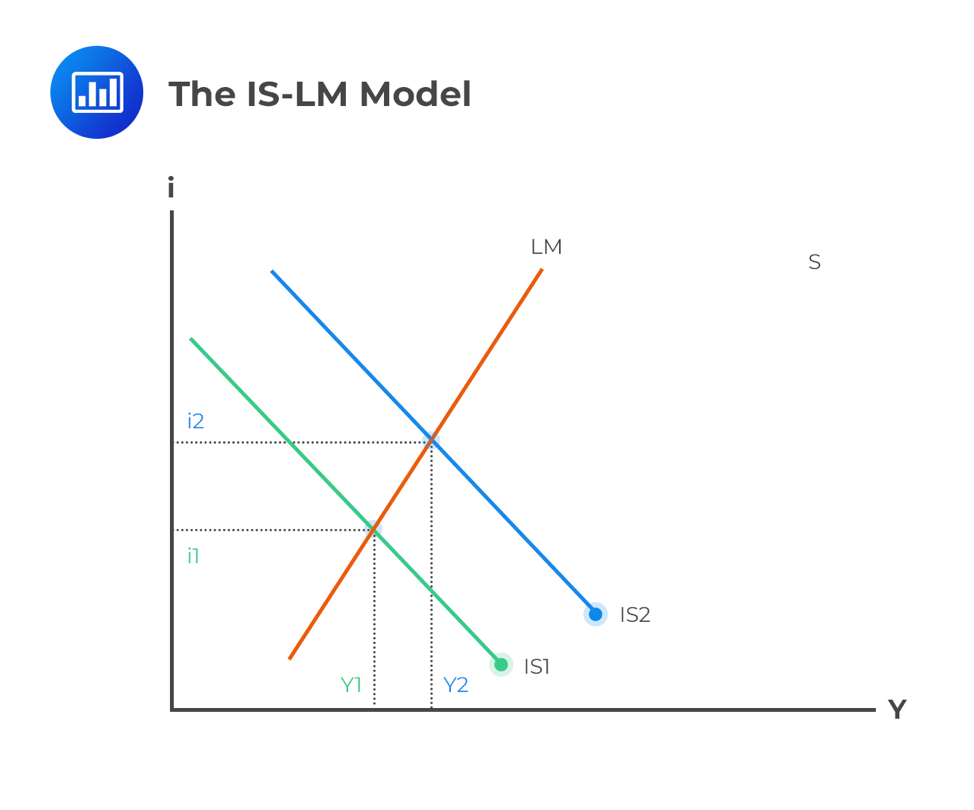



Is Lm Curves And Aggregate Demand Curve Cfa Level 1 Analystprep
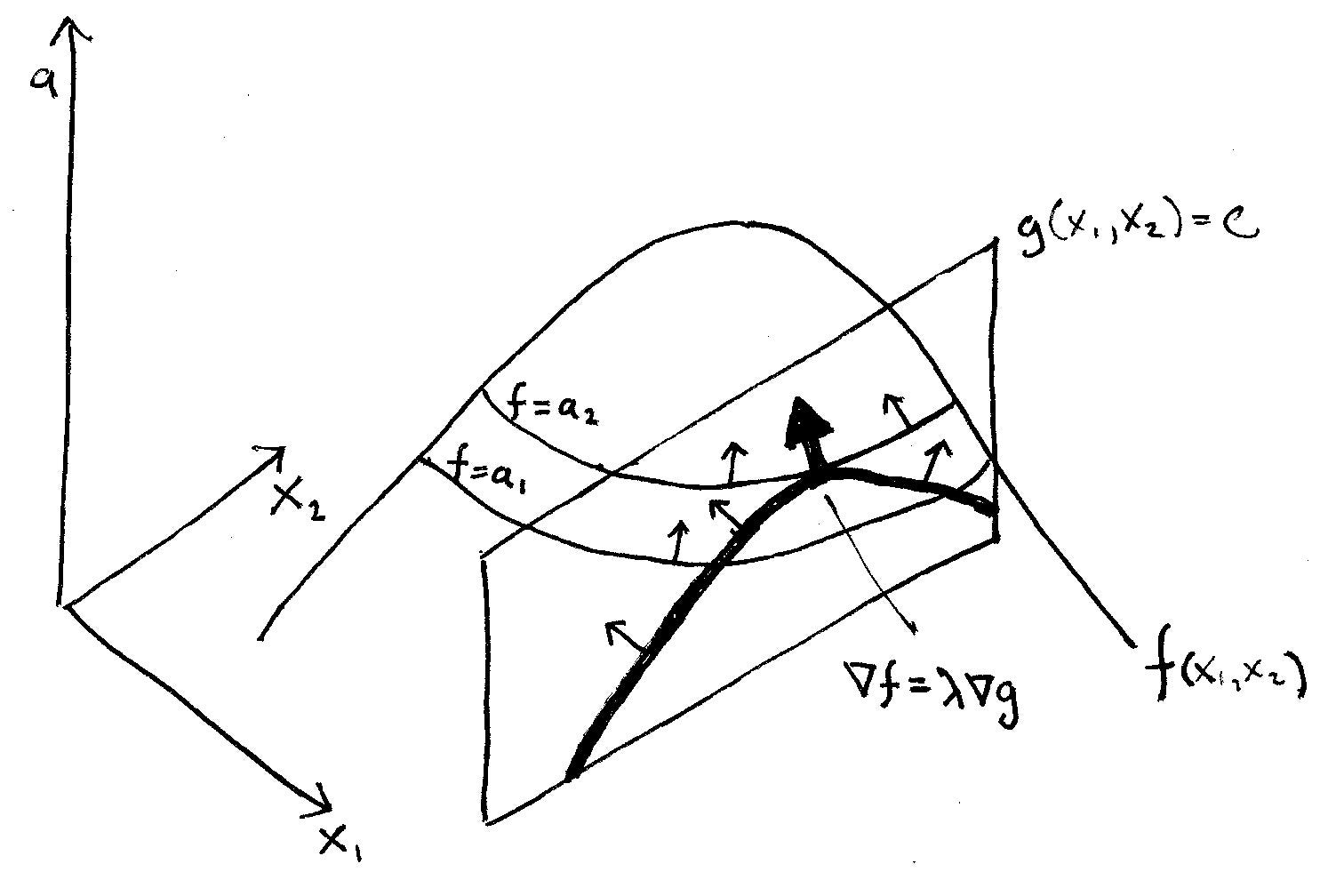



A Simple Explanation Of Why Lagrange Multipliers Works By Andrew Chamberlain Ph D Medium
/LafferCurve2-3509f81755554440855b5e48c182593e.png)



Laffer Curve Definition




Income And Substitution Effects Indifference Curve Economics Microeconomics Economics
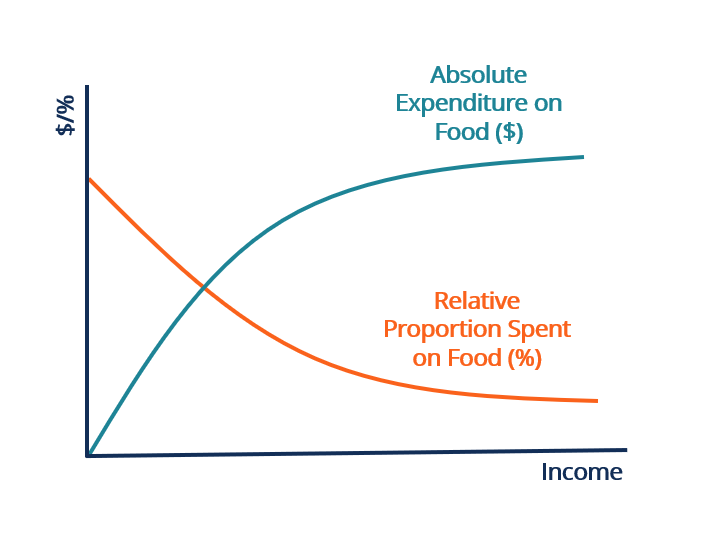



Engel S Law Overview Implications Engel S Curve
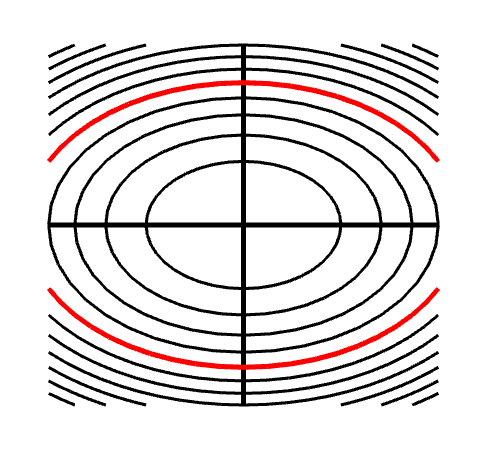



Level Sets Math Insight
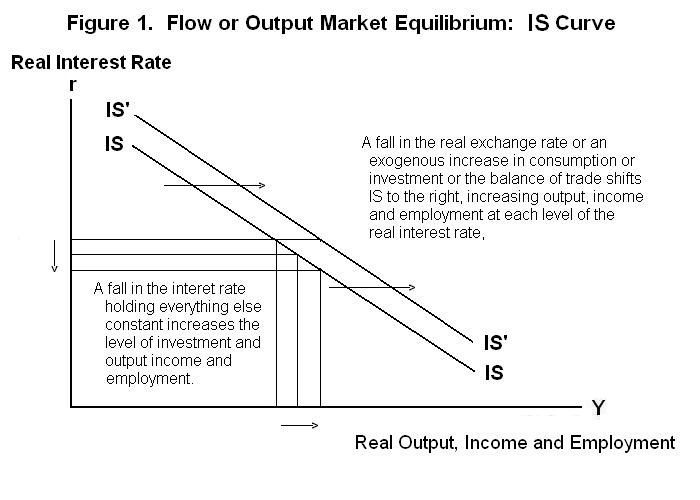



The Is And Lm Curves




Level Curves How To Draw Curves Economics Honours Mathematics Statistics Tuition Youtube




Flattening The Pandemic And Recession Curves Vox Cepr Policy Portal




Neoclassical And Keynesian Perspectives In The Ad As Model Macroeconomics



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿